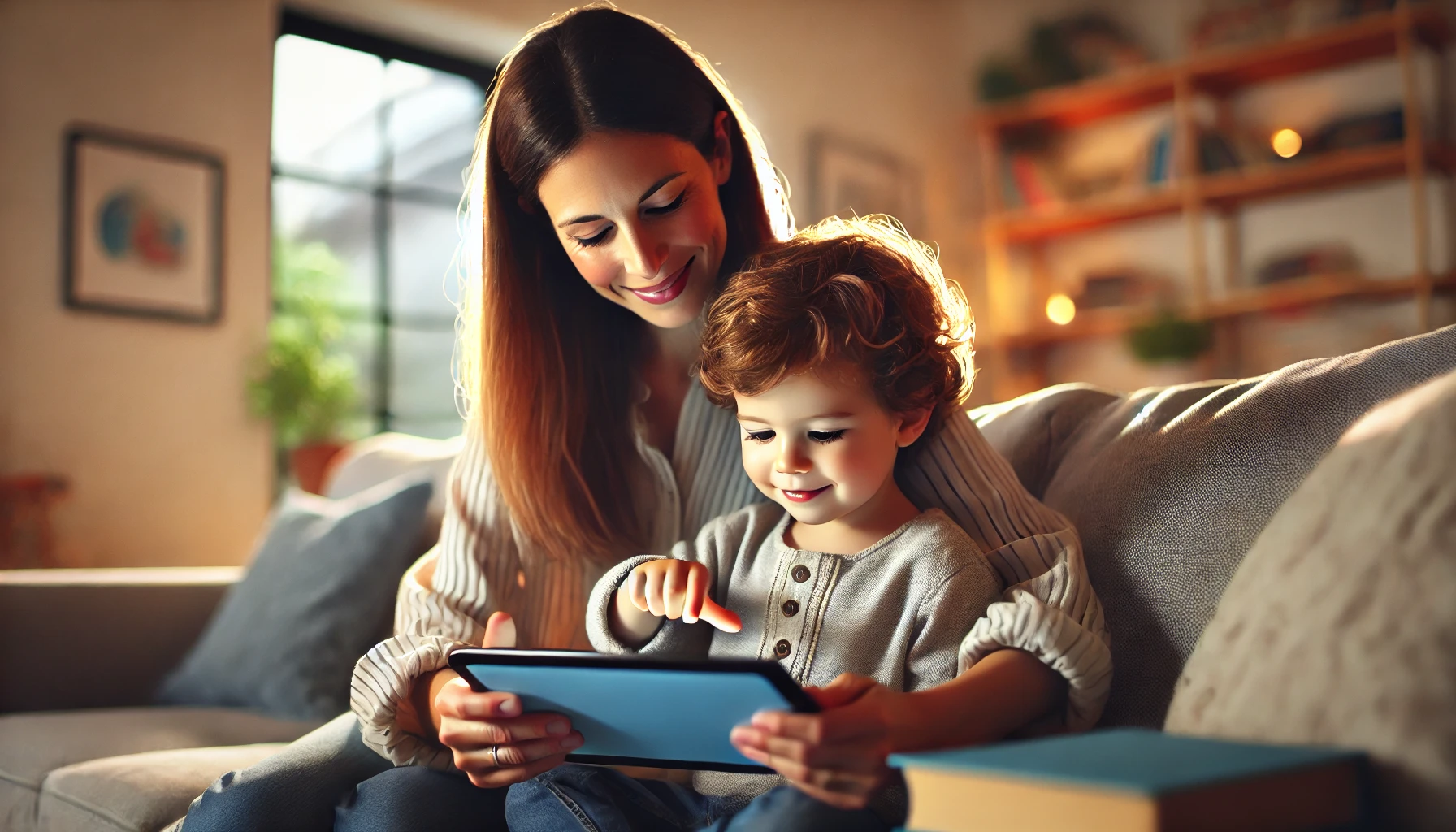
In today’s digital world, screens are an unavoidable part of daily life. From educational apps to entertainment, children are exposed to screens from an early age. While technology can be beneficial, excessive screen time can impact a child’s physical health, mental well-being, and social development.
Finding the right balance is key to ensuring that screen time is used effectively while promoting other essential activities like outdoor play, social interaction, and creative learning. In this article, we’ll explore expert-recommended screen time guidelines for different age groups and practical strategies to create a healthy digital routine.
Why Screen Time Needs to Be Managed
1. Supports Healthy Brain Development
Excessive screen time, especially in young children, can interfere with brain growth and delay language, motor, and social skills development.
2. Prevents Sleep Disruptions
The blue light emitted from screens suppresses melatonin, making it harder for children to fall asleep and affecting their overall sleep quality.
3. Reduces Risk of Behavioral Issues
Studies have linked prolonged screen exposure to attention problems, mood swings, and increased irritability in children.
4. Encourages Physical Activity
Children who spend too much time on screens tend to have sedentary lifestyles, increasing the risk of obesity and related health issues.
5. Enhances Social and Emotional Skills
Face-to-face interactions help children develop emotional intelligence, empathy, and communication skills—abilities that excessive screen time can hinder.
Screen Time Recommendations by Age
Experts, including the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), provide age-based guidelines for healthy screen use.
Infants (0-18 Months)
- Recommended screen time: None, except for video chatting with family.
- Why? Babies need real-world interactions for brain development. Passive screen time does not support cognitive growth at this stage.
- Alternatives: Reading books, tummy time, sensory play, and talking to your baby.
Toddlers (18-24 Months)
- Recommended screen time: Limited to 30 minutes per day of high-quality educational content.
- Why? Some exposure to educational media is acceptable, but real-world experiences are still more beneficial.
- Best Practices:
- Watch content together and discuss what they see.
- Avoid fast-paced, overstimulating programs.
Preschoolers (2-5 Years)
- Recommended screen time: Up to 1 hour per day of high-quality programming.
- Why? Interactive content can support learning, but excessive screen use can delay language and social skills.
- Best Practices:
- Prioritize co-viewing with parents or caregivers.
- Encourage active screen use, such as educational games instead of passive watching.
- Establish screen-free zones (e.g., bedrooms and mealtime areas).
School-Age Children (6-12 Years)
- Recommended screen time: No more than 2 hours of recreational screen time per day.
- Why? Excessive screen use can interfere with physical activity, homework, and sleep.
- Best Practices:
- Encourage screen-free play, hobbies, and outdoor activities.
- Monitor online content and teach internet safety.
- Implement a “no screens before bed” rule.
Teenagers (13-18 Years)
- Recommended screen time: No strict limit, but screen use should not interfere with sleep, exercise, schoolwork, or family time.
- Why? Teens use screens for social interaction, schoolwork, and entertainment, but balance is key.
- Best Practices:
- Set boundaries for recreational screen time.
- Encourage media literacy—help them analyze and question online content.
- Promote offline socialization and outdoor activities.
How to Create a Healthy Screen Time Routine
1. Set Clear Limits on Screen Use
Establish daily screen time limits based on age and responsibilities.
- Use parental controls to manage screen exposure.
- Create a family media plan that includes screen-free times (e.g., meals, family outings).
- Encourage a mix of screen-based and non-screen activities.
2. Prioritize High-Quality Content
Not all screen time is equal. Choose interactive, educational, and age-appropriate content.
- Look for apps and programs that encourage creativity, problem-solving, and learning.
- Avoid content with excessive violence, fast transitions, or overstimulating effects.
3. Encourage Active Screen Time
Engage children in activities that require participation rather than passive watching.
- Educational apps and learning platforms
- Creative tools like digital drawing, music composition, or coding games
- Family-friendly video games that promote teamwork and strategy
4. Establish Screen-Free Zones and Times
Creating designated screen-free areas helps children develop healthier habits.
- No screens during meals to encourage family conversation.
- No screens in bedrooms to improve sleep quality.
- No screens 1 hour before bedtime to support melatonin production.
5. Model Healthy Screen Habits
Children learn by example, so parents should demonstrate responsible screen use.
- Limit personal screen time in front of children.
- Prioritize in-person conversations over digital distractions.
- Engage in non-screen activities like reading, playing board games, or outdoor sports.
6. Balance Screen Time with Physical Activity
Encourage at least 60 minutes of active play per day to counteract sedentary screen use.
- Plan family activities like biking, hiking, or playing in the park.
- Use screen time as a reward for completing physical activities or chores.
7. Teach Digital Responsibility and Online Safety
As children grow, teaching them responsible screen use is essential.
- Discuss internet safety and set parental controls.
- Encourage critical thinking about online content.
- Monitor social media use and talk about online interactions.
Signs of Excessive Screen Time
If a child is spending too much time on screens, they may exhibit:
- Difficulty focusing on non-screen activities
- Increased irritability or mood swings
- Trouble falling or staying asleep
- Decreased interest in outdoor play or socializing
- Frequent headaches or eye strain
If these signs appear, gradually reduce screen exposure and encourage alternative activities.
Final Thoughts
Screens are a valuable tool when used appropriately, but excessive exposure can impact a child’s development. By following expert recommendations, setting clear boundaries, and encouraging a balance between screen time and real-world activities, parents can help children develop healthy digital habits that last a lifetime.